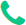
API stands for Application Programming Interface and it is set programming instructions and standards. APIs build integration of data into your supply chain, ensuring collaboration with different platforms and enabling real-time orchestration of processes across systems and enterprise. It let you access and integrate software applications. Real-time APIs instantly push data to endpoints, which can range from the actual endpoints of an API to external businesses or end-users. It allows different software programs to talk to each other without human interaction. Whenever a system wants to access a dataset from another application, it has to go through the API. The API is a middleman of sorts, accepting requests and, assuming the request is allowed, returning the data to the system that requested it.
How REAL-TIME APIs work
APIs collect the data and manage it. It helps to interpret the data. We can say that the APIs are the oil that keeps the cloud data machine running. APIs make often repeated fundamental to developer productivity and the complex processes which are highly reusable with a little bit of code. Each time we use a software application, computer, mobile device, or phone, this same complex web of API interaction is in play.
Benefits of Real-Time APIs
Monitoring systems: AS soon as the API consumer gets the data, they can start acting on it.
Market data & betting: the time from the event taking place to data being received is valuable in monetary terms.
Communications Users or systems interact in real-time where any lag in communication can represent a communications break down.
Collaborative experiences when one or more users are working together on a shared project, any missed or late changes can result in the duplicate effort and wasted time.
Real-time user experiences (UX) An action should give instant feedback; from pressing a button in a mobile app to unlock an IoT connected door to real-time chat, these experiences should be instantaneous.